What is Computer Hardware?
computer hardware is the physical components that a computer system requires to function. It encompasses everything with a circuit board that operates within a PC or laptop; including the motherboard, graphics card, CPU (Central Processing Unit), ventilation fans, webcam, power supply, and so on.
Although the design of hardware differs between desktop PCs and laptops due to their differences in size, the same core components will be found in both. Without hardware, there would be no way of running the essential software that makes computers so useful. Software is defined as the virtual programs that run on your computer; that is, operating system, internet browser, word-processing documents, etc
What is a Motherboard?
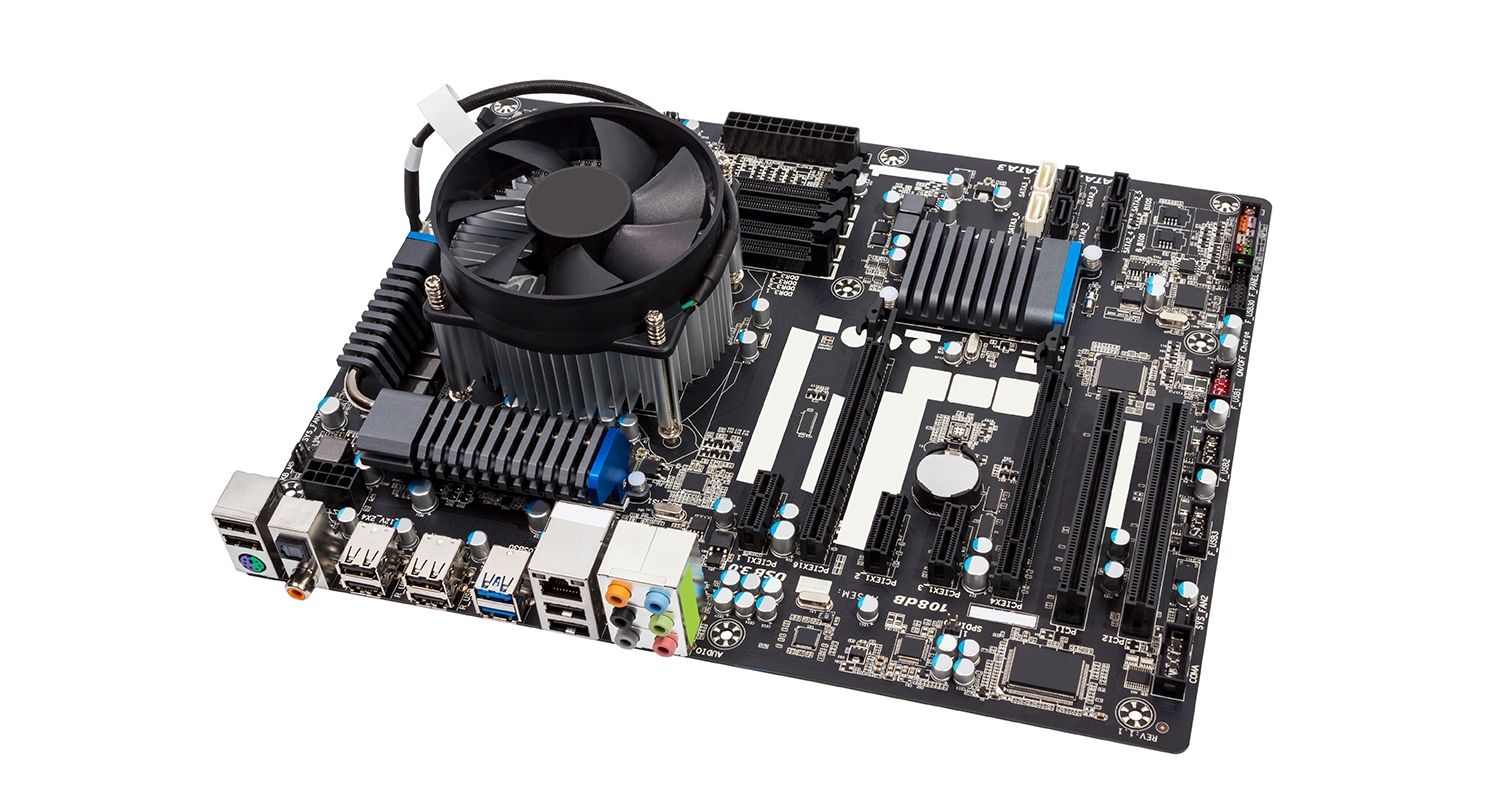

The motherboard is at the center of what makes a PC work. It houses the CPU and is a hub that all other hardware runs through. The motherboard acts as a brain; allocating power where it’s needed, communicating with and coordinating across all other components – making it one of the most important pieces of hardware in a computer.
When choosing a motherboard, it’s important to check what hardware ports the motherboard supplies. It’s vital to check how many USB ports, and what grade (USB 2.0, 3.0, 3.1) they are, as well as what display ports are used (HDMI, DVI, RGB) and how many of each there are. The ports on the motherboard will also help you define what other hardware will be compatible with your computer, such as what type of RAM and graphics card you can use.
Although the motherboard is just one piece of circuitry, it is home to another one of the most important pieces of hardware: the processor.
What is a CPU (Central Processing/Processor Unit)?
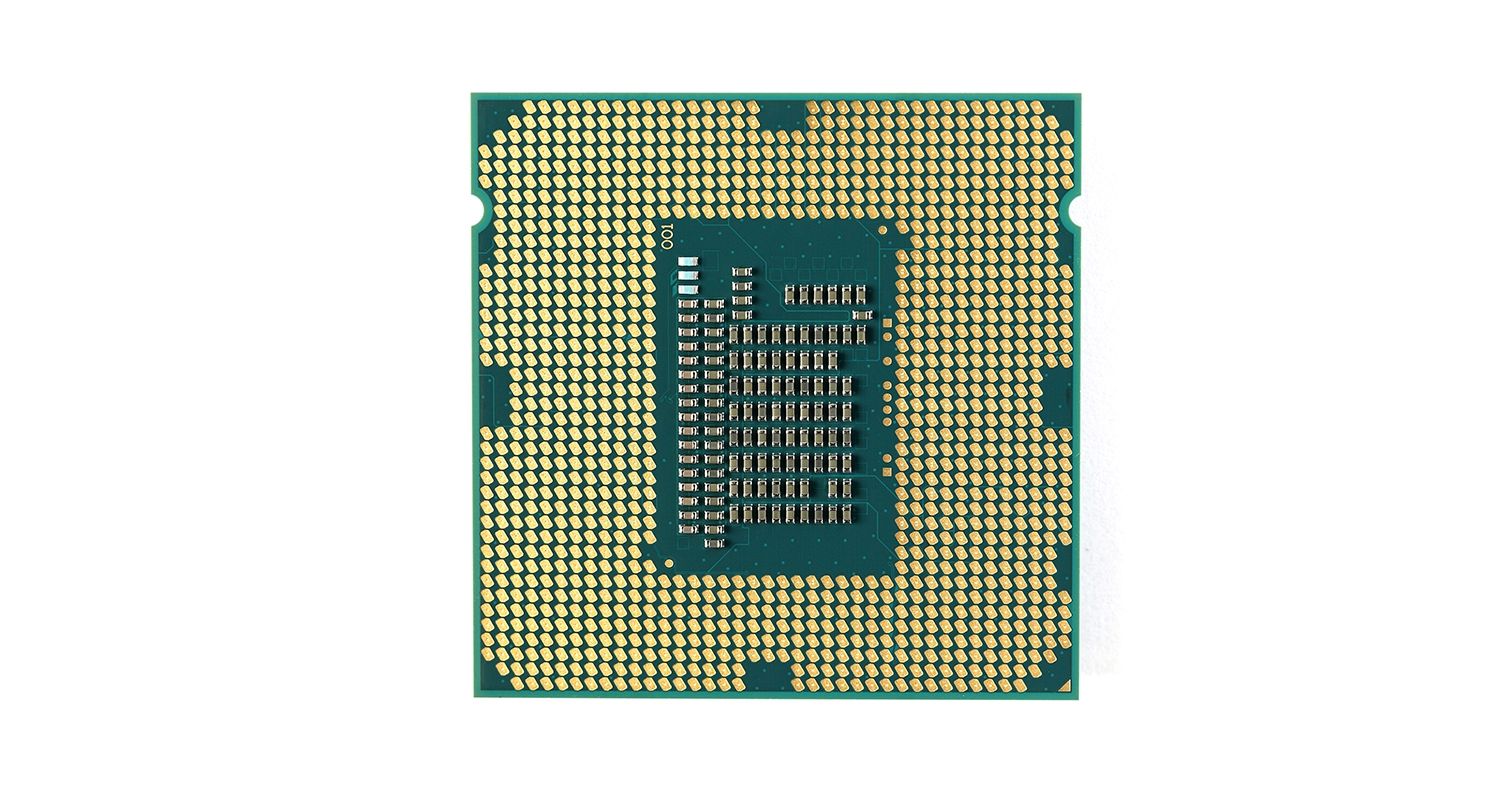

The CPU (Central Processing Unit or processor) is responsible for processing all information from programs run by your computer. The ‘clock speed’, or the speed at which the processor processes information, is measured in gigahertz (GHz). This means that a processor advertising a high GHz rating will likely perform faster than a similarly specified processor of the same brand and age.
What is RAM?
Random Access Memory, or RAM, is hardware found in the memory slots of the motherboard. The role of RAM is to temporarily store on-the-fly information created by programs and to do so in a way that makes this data immediately accessible. The tasks that require random memory could be; rendering images for graphic design, edited video or photographs, multi-tasking with multiple apps open (for example, running a game on one screen and chatting via Discord on the other).
How much RAM you require depends on the programs that you’ll be running. Medium intensity gaming generally uses 8GB of memory when performed alongside other programs, but video/graphic design can use upwards of 16GB of RAM. Find out how much memory your computer needs.
What is a Hard Drive?
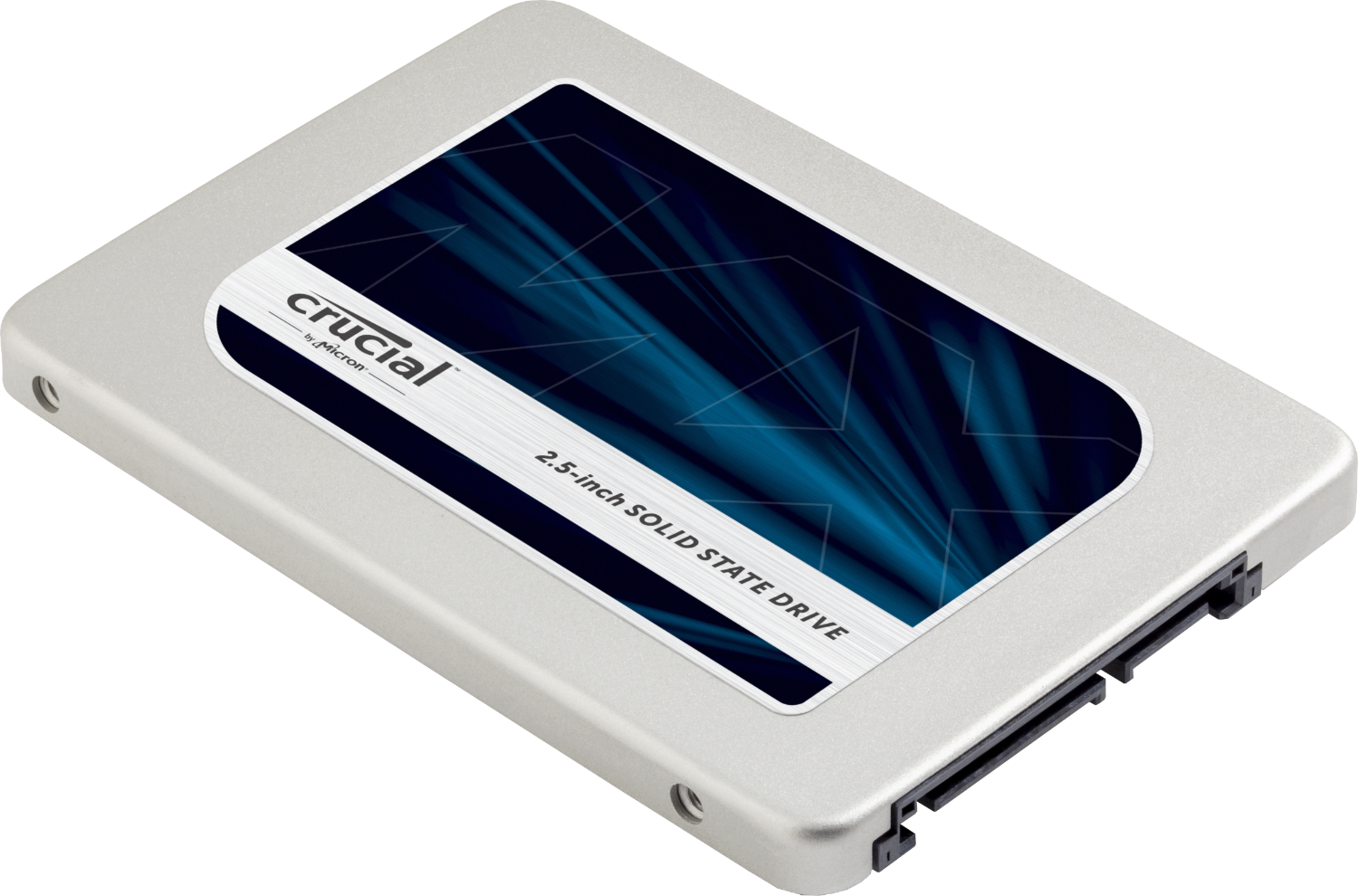
The hard drive is a storage device responsible for storing permanent and temporary data. This data comes in many different forms, but is essentially anything saved or installed to a computer: for example, computer programs, family photos, operating system, word-processing documents, and so on. Find out more about hard drives and how they work.
There are two different types of storage devices: the traditional hard disk drive (HDD) and the newer solid state drives (SSD). Hard disk drives work by writing binary data onto spinning magnetic disks called platters that rotate at high speeds, while a solid-state drive stores data by using static flash memory chips. Find out more about computer storage and how solid state drives work.

What is a Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)?
Especially important for 3D rendering, the GPU does exactly what its name suggests and processes huge batches of graphic data. You will find that your computer’s graphics card has at least one GPU. As opposed to the basic on-board graphic capabilities that PC motherboards supply, dedicated graphics cards interface with the motherboard via an expansion slot to work almost exclusively on graphic rendering. This also means you can upgrade your graphics card if you want to get a bit more performance from your PC.
Not only this, but modern GPUs fulfil a broad computational workload beyond just rendering, making them an extension to the central processing unit.

What is a Power Supply Unit (PSU)?
A power supply unit, commonly abbreviated as PSU, does more than just supply your computer with power. It is the point where power enters your system from an external power source and is then allocated by the motherboard to individual component hardware. Not all power supplies are made equally however, and without the right wattage PSU your system will fail to work.
A modern computer will generally need a PSU that’s rated between 500W – 850W to effectively power all hardware, although the size of the PSU will depend entirely on the power consumption of the system. Computers that are used for highly intensive tasks such as graphic design or gaming will require more powerful components and thus will need a bigger PSU to cater to this additional need.
Without the right amount of power, components won’t be able to run effectively and the computer might experience crashes or simply fail to boot at all. It’s recommended to have a power supply that more than covers your system usage. Not only do you guard yourself against system failure, you also future-proof yourself against needing a new PSU when you upgrade to more powerful PC components.
Understanding your computer and its hardware components can prove very useful when the time comes to upgrade or replace any parts, or when building a computer. Should a problem arise with the internal workings of your computer, you will have a better understanding of the importance of each component, the need for them to be in good working condition and how to go about solving any issues.

Hardware vs. Software


Software is a general term used to describe a collection of computer programs, procedures, and documentation that perform some task on a computer system. Practical computer systems divide software systems into three major classes: system software, programming software, and application software, although the distinction is arbitrary and often blurred. Software is an ordered sequence of instructions for changing the state of the computer hardware in a particular sequence. Software is typically programmed with a user-friendly interface that allows humans to interact more more efficiently with a computer system.
Computer - Software
Software is a set of programs, which is designed to perform a well-defined function. A program is a sequence of instructions written to solve a particular problem.
There are two types of software −
- System Software
- Application Software
System Software
The system software is a collection of programs designed to operate, control, and extend the processing capabilities of the computer itself. System software is generally prepared by the computer manufacturers. These software products comprise of programs written in low-level languages, which interact with the hardware at a very basic level. System software serves as the interface between the hardware and the end users.
Some examples of system software are Operating System, Compilers, Interpreter, Assemblers, etc.

Here is a list of some of the most prominent features of a system software −
- Close to the system
- Fast in speed
- Difficult to design
- Difficult to understand
- Less interactive
- Smaller in size
- Difficult to manipulate
- Generally written in low-level language
Application Software
Application software products are designed to satisfy a particular need of a particular environment. All software applications prepared in the computer lab can come under the category of Application software.
Application software may consist of a single program, such as Microsoft's notepad for writing and editing a simple text. It may also consist of a collection of programs, often called a software package, which work together to accomplish a task, such as a spreadsheet package.
Examples of Application software are the following −
- Payroll Software
- Student Record Software
- Inventory Management Software
- Income Tax Software
- Railways Reservation Software
- Microsoft Office Suite Software
- Microsoft Word
- Microsoft Excel
- Microsoft PowerPoint

Features of application software are as follows −
- Close to the user
- Easy to design
- More interactive
- Slow in speed
- Generally written in high-level language
- Easy to understand
- Easy to manipulate and use
- Bigger in size and requires large storage space
What are the differences between hardware and software?

Computer hardware is any physical device used in or with your machine, whereas software is a collection of code installed onto your computer's hard drive. For example, the computer monitor you are using to read this text and the mouse you are using to navigate this web page are computer hardware. The Internet browser that allowed you to visit this page and the operating system that the browser is running on are considered software.
Comparison chart
| Hardware | Software | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Devices that are required to store and execute (or run) the software. | Collection of instructions that enables a user to interact with the computer. Software is a program that enables a computer to perform a specific task, as opposed to the physical components of the system (hardware). |
| Types | Input, storage, processing, control, and output devices. | System software, Programming software, and Application software. |
| Function | Hardware serve as the delivery system for software solutions. The hardware of a computer is infrequently changed, in comparison with software and data, which are “soft” in the sense that they are readily created, modified, or erased on the comput | To perform the specific task you need to complete. Software is generally not needed to for the hardware to perform its basic level tasks such as turning on and reponding to input. |
| Examples | CD-ROM, monitor, printer, video card, scanners , label makers, routers and modems. | QuickBooks, Adobe Acrobat, Google Chrome, Microsoft Word, Microsoft Excel, Apple Maps |
| Inter dependency | Hardware starts functioning once software is loaded. | To deliver its set of instructions, Software is installed on hardware. |
| Failure | Hardware failure is random. Hardware does have increasing failure at the last stage. | Software failure is systematic. Software does not have an increasing failure rate. |
| Durability | Hardware wears out over time. | Software does not wear out over time. However, bugs are discovered in software as time passes. |
| Nature | Hardware is physical in nature. | Software is logical in nature. Create by Rajsushant |
You make so many great points here that I read your article a couple of times. This is great content for your readers.แทงบอลออนไลน์
ReplyDelete
ReplyDeleteI felt very happy while reading this site. This was really very informative site for me. I really liked it.KRT carts